Week1: The Call of Jeremiah and His Mission
Introduction and chapter 1
Week 1: The Call of Jeremiah and His Mission
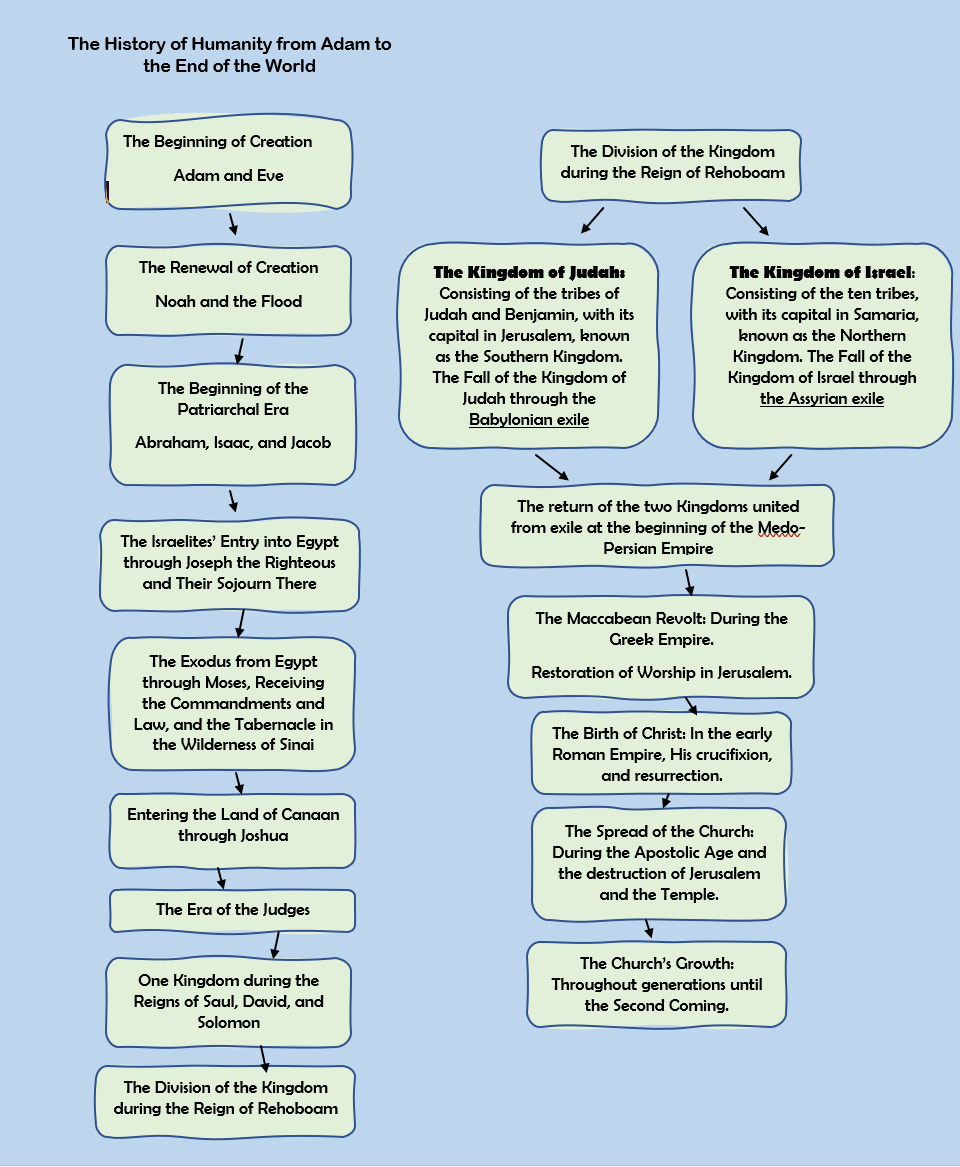
The History of Humanity from Adam to the End of the World
Introduction: Jeremiah the Prophet:
- The Old Testament contains 17 prophetic books (Splits into major and minor prophets based on the size of the book)
- Major Prophets (5 books): Isaiah, Jeremiah, Lamentations, Ezekiel, and Daniel
- Minor Prophets (12 books): Hosea, Joel, Amos, Obadiah, Jonah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah, Haggai, Zechariah, and Malachai
- Time of Birth:
- Jeremiah was born in the mid-seventh century BC during the reign of the wicked King Manasseh. Coming from a priestly family, Jeremiah was familiar with the Law and God’s works among His people. Having lived during the reigns of the wicked Manasseh and his equally wicked son Amon, Jeremiah witnessed the moral and spiritual corruption of both the king and the people. God later called him to confront these evils.
- The prophet Baruch was Jeremiah's disciple, who recorded many of his prophecies.
- Place of Birth:
- Jeremiah was born in the village of Anathoth, located northeast of Jerusalem
- God’s Call:
- God called Jeremiah to service through a vision when he was still young. His mission was to rebuke the evil of the king, leaders, priests, and people.
- Jeremiah lived a celibate life as commanded by the Lord.
- Titles:
- The Weeping Prophet: Known for his intense emotions, Jeremiah wept over the sins of those around him.
- The Job of the Prophets: Jeremiah endured intense suffering, including rejection by his people, betrayal by his own brother, physical torture, and imprisonment.
The Book of Jeremiah:
Introduction:
- Jeremiah addressed the Jews living in the southern kingdom, which consisted of the tribes of Judah and Benjamin, with Jerusalem as their capital.
- The people, led by corrupt leaders and wicked kings, were deeply sinful. Their unrepentance resulted in the Babylonian captivity and the destruction of Jerusalem and the temple.
- Jeremiah's message was a call to repentance, urging them to rely on God
Date:
- Jeremiah began his prophetic ministry in 626 BC, during King Josiah's reforms, and served for over 40 years. Despite being forcibly taken to Egypt, he continued urging repentance and faithfulness to God until his martyrdom by stoning in Egypt.
Jeremiah the prophet lived during the reigns of several kings
- Manasseh the Wicked
- Amon the Wicked
- Josiah the Righeous
- Jehoahaz the Wicked
- Jehoiakim (brother of Jehoahaz) the Wicked
- Jehoiachin
- Zedekiah
How Did the Babylonian Captivity Happen?
- As the Assyrian Empire weakened, King Josiah of Jerusalem gained independence but was killed by Necho, king of Egypt, in the Battle of Megiddo.
- Necho deposed Josiah's son Jehoahaz, replacing him with Jehoiakim, who taxed the people heavily to pay tribute to Egypt.
- Nebuchadnezzar defeated Necho, leading Jehoiakim to ally with Babylon. Jeremiah warned against reliance on Egypt and urged repentance.
- Nebuchadnezzar captured Jerusalem, exiled King Jehoiachin, and installed Zedekiah as king.
The Babylonian captivity occurred in three stages:
- 605 BC, during King Jehoiakim’s reign (Daniel and the three young men were exiled)
- 597 BC, during King Jehoiachin’s reign (Great Exile, Ezekiel and Mordecai exiled)
- 587 BC, When King Zedekiah was captured and exiled to Babylon (Jeremiah was exiled)
- After Zedekiah's exile, the King of Babylon came and burned the temple and destroyed the walls of Jerusalem.
Objectives of the Book of Jeremiah:
- Call to Repentance: Urging the people to return to God.
- God’s Discipline and Mercy: Highlighting that God disciplines His children when they sin but also affirms His mercy.
- Need for the Messiah: Pointing to the hope of the coming Savior.
- Spiritual Principles:
- Sin is a breach of the covenant with God.
- All sins against others are ultimately offenses against God.
- Times of hardship should lead to self-examination and renewed commitment to God.
Outline:
- The Call of Jeremiah and His Mission (Chapter 1).
- Prophecies Before the Fall of Jerusalem and the Promise of Return from Exile (Chapters 2–33).
- The History of the Fall of Jerusalem (Chapters 34–45).
- Prophecies Concerning the Nations (Chapters 46–51).
- Conclusion: Review of the Events of the Exile (Chapter 52).
Reading:
The Book of Jeremiah: Chapter 1
Outline:
- Introduction to the Prophet and the History of His Prophethood (1:1-3)
- The Call of Jeremiah (1:4-10)
- Vision of a Branch of Almond tree and the Boiling Pot (1:11-16):
- Jeremiah's Responsibility (1:17-19)
Resources:
- Father Luke Maher - Audio (Arabic)
- Father Dawood Lemay- Audio (Arabic)
- Commentary on the Book of Jeremiah (English) Fr. Tadros Malaty. PDF: 024_Jeremiah.pdf
Key verse(s):
"They will fight against you, But they shall not prevail against you. For I am with you, says the Lord, to deliver you.." Jeremiah 1:19
Comments:
1. Introduction to the Prophet and the History of His Prophethood (1:1-3)
- Prophet Jeremiah: son of Hilkiah the priest, born in Anathoth (tribe of Benjamin).
- Beginning of his writing during the reign of King Josiah over Judah (capital: Jerusalem).
- The Kingdom of Judah included the tribes of Judah and Benjamin.
- Jeremiah’s prophethood continued during the reigns of Kings Jehoiakim and Zedekiah.
- The exile occurred in the 11th year of Zedekiah's reign.
2. The Call of Jeremiah (1:4-10)
- God's message began to Jeremiah, informing him that he was chosen for service even before he was formed in his mother's womb.
- "He chose us in Him before the foundation of the world, that we should be holy and without blame before Him in love" (Ephesians 1:4).
- Contemplation: God loved us and consecrated us to live for Him. We shouldn’t become distracted by worldly concerns and deviate from Him through many sins, but we should please Him in everything and serve Him faithfully.
- Jeremiah expressed his inability to carry out God’s call to him, referring to himself as "a youth," meaning he was younger than thirty, the age at which Jews considered a man fully mature. This is the same age at which Jesus began His ministry. But God supported Jeremiah and promised to save him and be with him to complete his service.
- God touched Jeremiah’s lips to give him the strength to speak God’s word.
3. Vision of a Branch of Almond tree and the Boiling Pot (Jeremiah 1:11-16):
- Branch of Almont Tree: The first vision given to Jeremiah is of an almond rod, which symbolizes God's watchfulness and care. The almond tree appears lifeless in winter but bears fruit in spring. God watches His people but their sin will lead to punishment if they don’t repent.
- The Boiling Pot: The second vision that Jeremiah saw was a boiling pot, which symbolizes the pride of the Jews. They believed that as long as the temple of God was among them and they had outward forms of personal worship, no harm would come to them. However, the pot's mouth facing north symbolizes the Babylonian attack from the north on Jerusalem and Judah, leading to its occupation and destruction.
- The visions remind God's people to heed His word, repent, and avoid neglecting His commands, lest they face punishment.
4. Jeremiah's Responsibility (1:17-19)
- God reminded him that the most important fear is of God, not the fear of people.
- God promised to make Jeremiah:
- Fortified City: to be protector to those who fear him
- Iron Pillar: strong foundation
- Bronze Wall: protection from oppositions of th wicked
Review/recap questions:
**Servant may add more questions
- List Major and minor prophets? What's the difference between them?
- Who is the prophet Jeremiah?
- How Did the Babylonian Captivity Happen?
- What was God response to Jeremiah when he said “I cannot speak for I am a youth”?
- What is the meaning of the two visions of Jeremiah?
Homework:
**Servant may add more questions
- Before I ______ you in the womb, I ______ you. Before you were ______ -I sanctified you. I ordained you a ______ to the nations."
- What are the two visions of Jeremiah?. Explain
- "Do not say I am a youth." Who said this sentence? To whom? Why?
No comments to display
No comments to display