Week1: The Call of Jeremiah and His Mission
Introduction and chapter 1
Week 1: The Call of Jeremiah and His Mission
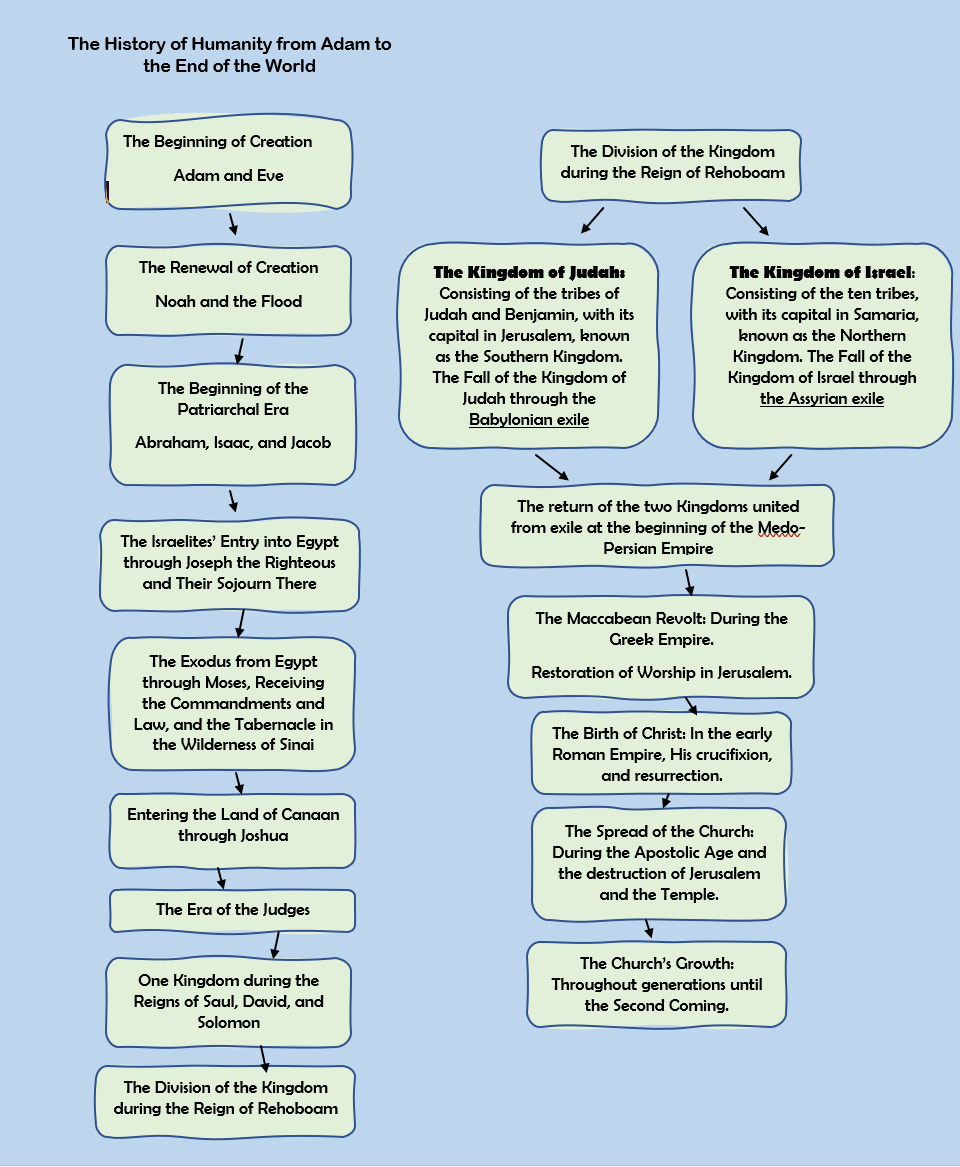
The History of Humanity from Adam to the End of the World
Introduction: Jeremiah the Prophet:
- Time of Birth:
- Jeremiah was born in the mid-seventh century BC during the reign of the wicked King Manasseh. Coming from a priestly family, Jeremiah was familiar with the Law and God’s works among His people. Having lived during the reigns of the wicked Manasseh and his equally wicked son Amon, Jeremiah witnessed the moral and spiritual corruption of both the king and the people. God later called him to confront these evils.
- The prophet Baruch was Jeremiah's disciple, who recorded many of his prophecies.
- Place of Birth:
- Jeremiah was born in the village of Anathoth, located northeast of Jerusalem
- God’s Call:
- God called Jeremiah to service through a vision when he was still young. His mission was to rebuke the evil of the king, leaders, priests, and people.
- Jeremiah lived a celibate life as commanded by the Lord.
- Titles:
- The Weeping Prophet: Known for his intense emotions, Jeremiah wept over the sins of those around him.
- The Job of the Prophets: Jeremiah endured intense suffering, including rejection by his people, betrayal by his own brother, physical torture, and imprisonment.
The Book of Jeremiah:
Introduction:
- Jeremiah addressed the Jews living in the southern kingdom, which consisted of the tribes of Judah and Benjamin, with Jerusalem as their capital.
- The people, led by corrupt leaders and wicked kings, were deeply sinful. Their unrepentance resulted in the Babylonian captivity and the destruction of Jerusalem and the temple.
- Jeremiah's message was a call to repentance, urging them to rely on God
Date:
- Jeremiah began his prophetic ministry in 626 BC, during King Josiah's reforms, and served for over 40 years. Despite being forcibly taken to Egypt, he continued urging repentance and faithfulness to God until his martyrdom by stoning in Egypt.
Jeremiah the prophet lived during the reigns of several kings
- Manasseh the Wicked
- Amon the Wicked
- Josiah the Righeous
- Jehoahaz the Wicked
- Jehoiakim (brother of Jehoahaz) the Wicked
- Jehoiachin
- Zedekiah
How Did the Babylonian Captivity Happen?
- As the Assyrian Empire weakened, King Josiah of Jerusalem gained independence but was killed by Necho, king of Egypt, in the Battle of Megiddo.
- Necho deposed Josiah's son Jehoahaz, replacing him with Jehoiakim, who taxed the people heavily to pay tribute to Egypt.
- Nebuchadnezzar defeated Necho, leading Jehoiakim to ally with Babylon. Jeremiah warned against reliance on Egypt and urged repentance.
- Nebuchadnezzar captured Jerusalem, exiled King Jehoiachin, and installed Zedekiah as king.
The Babylonian captivity occurred in three stages:
- 605 BC, during King Jehoiakim’s reign (Daniel and the three young men were exiled)
- 597 BC, during King Jehoiachin’s reign (Great Exile, Ezekiel and Mordecai exiled)
- 587 BC, When King Zedekiah was captured and exiled to Babylon (Jeremiah was exiled)
- After Zedekiah's exile, the King of Babylon came and burned the temple and destroyed the walls of Jerusalem.
Objectives of the Book of Jeremiah:
- Call to Repentance: Urging the people to return to God.
- God’s Discipline and Mercy: Highlighting that God disciplines His children when they sin but also affirms His mercy.
- Need for the Messiah: Pointing to the hope of the coming Savior.
- Spiritual Principles:
- Sin is a breach of the covenant with God.
- All sins against others are ultimately offenses against God.
- Times of hardship should lead to self-examination and renewed commitment to God.
Outline:
- The Call of Jeremiah and His Mission (Chapter 1).
- Prophecies Before the Fall of Jerusalem and the Promise of Return from Exile (Chapters 2–33).
- The History of the Fall of Jerusalem (Chapters 34–45).
- Prophecies Concerning the Nations (Chapters 46–51).
- Conclusion: Review of the Events of the Exile (Chapter 52).